- Understanding flexibility and muscle tension
- The science behind massage and muscle mechanics
- Massage techniques that improve flexibility
- Improved blood flow and oxygenation
- Reduction of muscle tone and tension
- The role of fascia in flexibility
- Massage and neural adaptation
- Massage for injury recovery and scar tissue management
- Psychological impact on flexibility
- Integrating massage into flexibility training
- Long-term benefits of massage for flexibility
- Restoring movement through mindful touch
Flexibility is one of the cornerstones of physical health, influencing everything from posture and mobility to athletic performance and injury prevention. Whether you’re an athlete striving for optimal performance or an office worker combating stiffness from long hours at a desk, maintaining supple muscles is essential. Among the various methods used to improve flexibility, massage therapy stands out as both a preventive and restorative approach. It doesn’t simply make you feel relaxed; it produces measurable physiological changes that enhance muscle elasticity, reduce stiffness, and improve overall movement efficiency.
This article explores how massage affects muscle flexibility, examining its impact on muscle fibres, connective tissue, and circulation, while explaining why regular treatments can make a long-term difference to mobility and wellbeing.
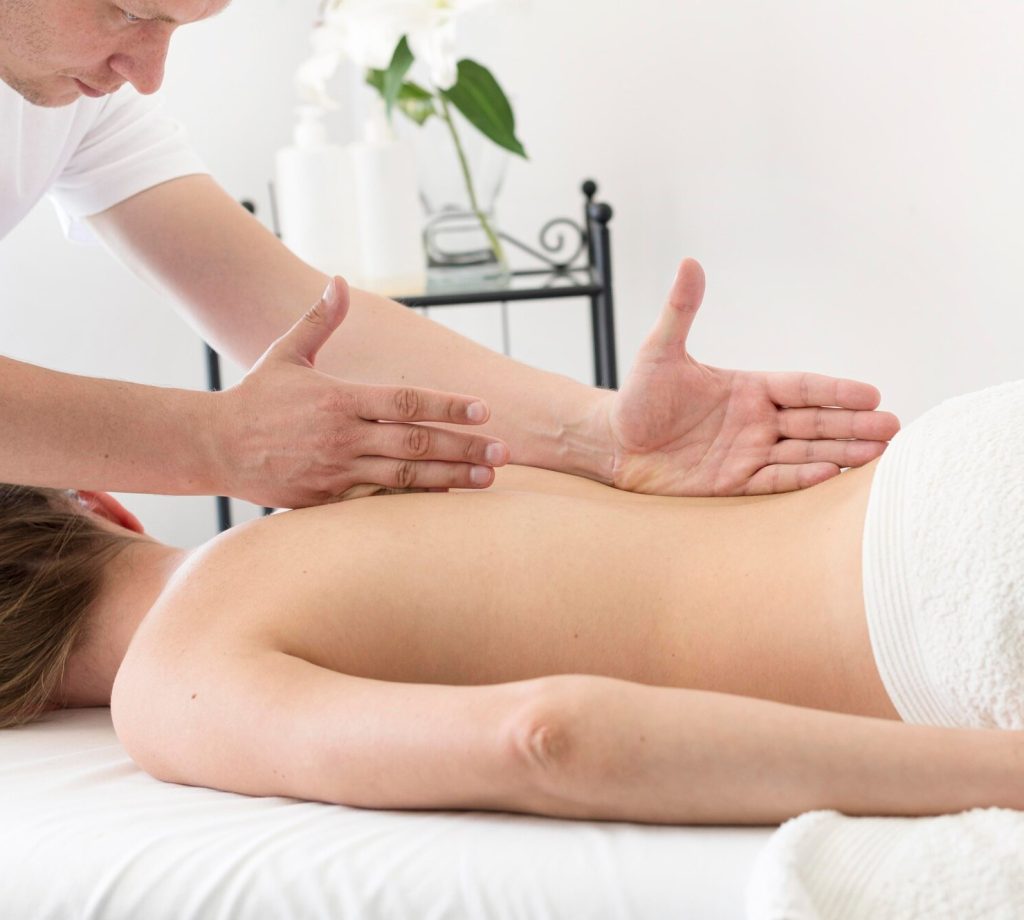

flexibility and muscle
Understanding flexibility and muscle tension
Flexibility refers to the ability of muscles and joints to move through their full range of motion without discomfort or restriction. It depends on the length and elasticity of muscle fibres, the health of connective tissues (such as fascia and tendons), and the lubrication within the joints.
However, modern lifestyles often work against flexibility. Sedentary habits, repetitive movements, stress, and poor posture contribute to muscle shortening and tension. When muscles remain contracted for extended periods, they lose elasticity, leading to stiffness, discomfort, and a greater risk of strain.
Over time, tight muscles can pull on joints and alter body alignment, causing compensatory movement patterns that further reduce flexibility. Stretching alone can help, but massage therapy complements these efforts by addressing the root causes of tightness within the muscular and fascial systems.
muscle mechanics
The science behind massage and muscle mechanics
To understand how massage enhances flexibility, it’s essential to look at what happens beneath the surface. Muscles are made up of bundles of fibres surrounded by connective tissue called fascia. When muscles are overused, underused, or injured, these fibres can develop adhesions, areas where tissue sticks together instead of sliding smoothly. These adhesions restrict movement and reduce elasticity.
Massage works by applying pressure, friction, and movement across these fibres, physically breaking down adhesions and realigning the tissue structure. This process restores normal glide between muscle layers, allowing for freer movement and improved flexibility.
Additionally, massage stimulates blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles, which helps repair microtears, remove metabolic waste such as lactic acid, and maintain optimal hydration within tissues, all of which are key to preserving suppleness.
therapeutic benefits
Massage techniques that improve flexibility
Deep Tissue Massage – focuses on the deeper layers of muscle and fascia, helping to release chronic tension and realign fibres.
Sports Massage – combines deep pressure, stretching, and friction techniques to enhance mobility and prevent injury, making it popular among athletes.
Myofascial Release – specifically targets the fascia, the connective tissue that surrounds muscles, to restore its elasticity and reduce restrictions.
Swedish Massage – while gentler, promotes circulation and relaxation, which indirectly aids flexibility by reducing muscle tone and allowing greater range of motion.
Each of these techniques stimulates the nervous system and circulatory system differently, but all share the goal of improving the quality and responsiveness of muscle tissue.
improved blood flow
Improved blood flow and oxygenation
One of the most immediate effects of massage on muscle flexibility is enhanced circulation. The mechanical pressure applied during massage dilates blood vessels, increasing the flow of oxygen-rich blood to muscles. This delivers essential nutrients that support muscle repair and removes metabolic waste that can cause stiffness and fatigue.
With improved oxygenation, muscles remain pliable and better able to contract and relax efficiently. In contrast, poor circulation leads to stagnation, a build-up of toxins and lack of nutrients that causes muscles to harden and lose elasticity.
Regular massage keeps the tissues hydrated and nourished, preventing the micro-adhesions and stiffness that typically occur after prolonged inactivity or intense physical effort.
reduction of muscle
Reduction of muscle tone and tension
Muscle tone, the state of partial contraction that keeps muscles ready for action, can become excessive due to stress, overtraining, or repetitive strain. When muscle tone is too high, the body experiences constant tightness and reduced flexibility.
Massage reduces this tension by stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system, which triggers the body’s relaxation response. As the nervous system calms, muscle fibres loosen and lengthen naturally. This immediate release of tension allows for a greater range of motion and more fluid movement.
For athletes, this is particularly valuable before or after training sessions, as relaxed muscles are more resilient and less prone to injury. For office workers, it alleviates chronic tightness in the shoulders, neck, and back caused by prolonged sitting.
ascia in flexibility
The role of fascia in flexibility
When people think of flexibility, they often focus solely on muscles, but fascia, the web-like connective tissue that surrounds and interlinks muscles, plays an equally important role. Healthy fascia is smooth and pliable, allowing muscle fibres to move freely. However, dehydration, lack of movement, or injury can cause fascia to become sticky and restrictive.
Massage, particularly myofascial release, restores the elasticity of fascia by stretching and mobilising it. The slow, sustained pressure used in these techniques warms and hydrates the tissue, reducing stiffness and improving coordination between muscle groups.
When fascia is released, movement feels more effortless, posture improves, and flexibility increases without the need for excessive stretching.
neural adaptation
Massage and neural adaptation
Flexibility is not only a mechanical issue, it’s also neurological. The nervous system regulates how far muscles can stretch by sending signals to contract when they reach a perceived limit. This protective reflex, known as the stretch reflex, prevents injury but can also limit mobility when overly sensitive.
Massage influences the nervous system by reducing the excitability of these protective reflexes. The slow, rhythmic pressure applied during massage encourages the brain to perceive stretching and movement as safe, gradually allowing muscles to extend further.
Over time, this retraining of the nervous system helps increase flexibility naturally, without forcing the muscles beyond their comfort zone.
massage for injury
Massage for injury recovery and scar tissue management
Flexibility is often compromised after injuries such as strains, sprains, or surgeries. During the healing process, the body forms scar tissue to repair damaged muscle fibres. However, this tissue is less elastic than healthy muscle and can limit movement if it builds up excessively.
Massage therapy helps remodel scar tissue by breaking down adhesions and aligning new collagen fibres in the direction of normal movement. This controlled pressure encourages proper healing, restores mobility, and prevents chronic stiffness.
For individuals recovering from injuries, massage is often used alongside physiotherapy or stretching programmes to accelerate rehabilitation and restore full range of motion safely.
impact on flexibility
Psychological impact on flexibility
Although flexibility is largely physical, the mind plays a crucial role. Stress, anxiety, and emotional tension can lead to muscle tightness, particularly in the shoulders, neck, and lower back. Massage addresses both physical and emotional aspects by reducing stress hormones like cortisol and promoting relaxation through endorphin release.
When the mind relaxes, the body follows. Muscles become less guarded, allowing them to stretch and move more freely. This holistic connection between emotional state and physical flexibility explains why regular massage not only improves physical performance but also enhances overall wellbeing.
flexibility training
Integrating massage into flexibility training
While massage is powerful on its own, it delivers the best results when combined with stretching, mobility exercises, and proper hydration. For those seeking long-term improvements, integrating massage into a regular training routine ensures that muscles remain balanced and healthy.
An effective routine might include:
- weekly self-massage or foam rolling to release superficial tension,
- monthly professional sessions for deeper muscular or fascial work,
- daily stretching and mobility exercises to reinforce flexibility gains achieved through massage.
massage for flexibility
Long-term benefits of massage for flexibility
The effects of massage on flexibility are both immediate and cumulative. After just one session, most people notice a feeling of looseness, ease of movement, and reduced stiffness. Over time, consistent treatments help recondition the muscles and connective tissues, preventing the recurrence of tightness.
For athletes, this translates to improved performance, reduced injury risk, and faster recovery between workouts. For those with sedentary jobs or chronic tension, regular massage helps maintain posture, alleviate pain, and support joint health.
Furthermore, massage improves body awareness, clients learn to recognise early signs of tension and respond proactively, preventing the cycle of tightness and stiffness from taking hold again.
restoring movement
Restoring movement through mindful touch
Massage affects muscle flexibility through a complex interplay of physiological and neurological mechanisms. By improving circulation, reducing muscle tone, mobilising fascia, and calming the nervous system, it restores the body’s natural ability to move freely and efficiently.
Whether used as part of an athlete’s recovery routine, a rehabilitation programme, or a self-care regimen for everyday life, massage provides both immediate relief and long-term benefits. It teaches the body to let go of restriction and the mind to trust movement again.
True flexibility is not just about stretching muscles, it’s about creating harmony between structure, function, and relaxation. Massage achieves this balance through the healing power of touch, transforming stiffness into freedom of motion and tension into effortless grace.
Massage Treatments
Check out our massages
Choose the right massage for you and combine relaxation with therapy for your body and muscles.
If you need help, contact me!

